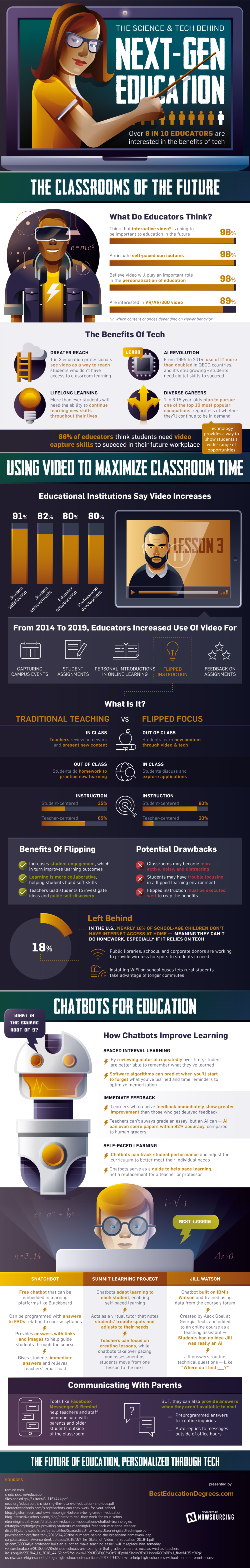
Educators are tapping into the digital revolution and adopting new technologies to help students reach their full potential, but can they adapt quickly enough to prepare children for the changing future of work?
The Growing Role of Tech in Classrooms
Today’s infographic from Best Education Degrees explores the different ways technology is transforming classrooms, and disrupting education as we know it.
The Next Generation
Although some might view technology as pervasive, for younger generations, it is ever-present. Children and young adults make up one-third of all internet users, so it’s no surprise that they are more hyper-connected and digitally savvy than their parents. The combination of evolving educational needs for children and a more uncertain future of work means that updating what children learn, and how they learn it, has become a crucial issue for schools and colleges—but what should be prioritized?
Classrooms 2.0
In a survey of 1,400 educators, the majority of them say they believe that classrooms of the future will be centered around self-paced and personalized learning. This student-centric approach would allow children to choose their own pace and learning objectives based on individual interests—all of which could be guided by artificial intelligence, chatbots, and video-based learning.
Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence in education typically focuses on identifying what a student does or doesn’t know, and then subsequently developing a personalized curricula for each student. The AI-powered language learning platform Duolingo is one of the most downloaded education apps globally, with more than 50 million installs in 2018. The platform single-handedly challenges the notion of traditional learning, with a study showing that spending just 34 hours on the app equates to an entire university semester of language education. AI-driven applications in education are still in their infancy, but Duolingo’s success demonstrates the growth potential in the sector. In fact, the nascent market for AI in education is expected to reach $6 billion by the year 2025. Over half of this will come from China and the U.S., with China leading globally.
Chatbots
Chatbots are also quickly becoming a fundamental tool in next generation education. Designed to simplify the interaction between student and computer, chatbots provide a wide range of benefits, including:
Spaced interval learning: Uses algorithms and repetition to optimize memorization Immediate feedback: Papers can be graded with 92% accuracy and in a faster time than teachers Self-paced learning: Tracks a student’s performance and guides them based on their individual needs
This innovative technology is arming educators with new strategies for more engaged learning, whilst simultaneously reducing their workload.
Video Learning
Although video-based learning may not necessarily be considered as innovative as artificial intelligence or chatbots, 98% of educators view it as a vital component in personalized learning experiences. Most institutions report incorporating video into their curriculums in some way, but even higher demand for video-based learning may come from students in the near future. This is due to the fact that video learning increases student satisfaction by 91%, and student achievements by 82%, which could be why educators are increasingly using video for tasks like:
Providing material for student assignments Giving feedback on assignments Flipped instruction (blended learning) exercises
A flipped classroom overturns conventional learning by focusing on practical content that is delivered online and often outside the classroom.
The Battle Between Traditional and Tech
Flipping classrooms is a trend that has gained momentum in recent years—and may be considered to be a radical change in how students absorb information. The relatively new model also eliminates homework, by empowering students to work collaboratively on their tasks during class time. Although new models of learning are disrupting the status quo of traditional learning, could the increasing amount of time children spend in front of screens be detrimental? Research has shown that children are more likely to absorb information from books rather than screens. There has also been an evident increase in low-tech or tech-free schools that believe that human interaction is paramount when it comes to keeping children engaged and excited to learn.
Creating First-Class Humans
Although we may not be in the era of iTeachers just yet, the benefits of technology as teaching aids are undeniable. However, what is more important is that these aids are used in tandem with developmental and educational psychology—ultimately keeping students rather than technology at the core of education. —OECD, Trends Shaping Education report After all, how children develop these skills is perhaps less important than their ability to navigate change, as that is the only thing that will remain constant. on But fast forward to the end of last week, and SVB was shuttered by regulators after a panic-induced bank run. So, how exactly did this happen? We dig in below.
Road to a Bank Run
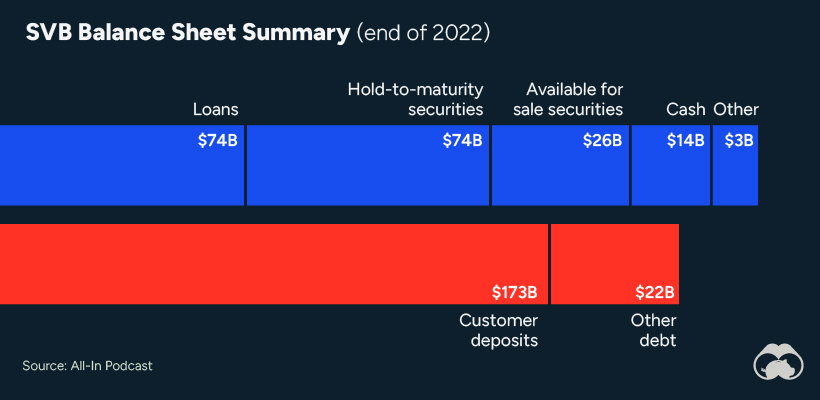
SVB and its customers generally thrived during the low interest rate era, but as rates rose, SVB found itself more exposed to risk than a typical bank. Even so, at the end of 2022, the bank’s balance sheet showed no cause for alarm.
As well, the bank was viewed positively in a number of places. Most Wall Street analyst ratings were overwhelmingly positive on the bank’s stock, and Forbes had just added the bank to its Financial All-Stars list. Outward signs of trouble emerged on Wednesday, March 8th, when SVB surprised investors with news that the bank needed to raise more than $2 billion to shore up its balance sheet. The reaction from prominent venture capitalists was not positive, with Coatue Management, Union Square Ventures, and Peter Thiel’s Founders Fund moving to limit exposure to the 40-year-old bank. The influence of these firms is believed to have added fuel to the fire, and a bank run ensued. Also influencing decision making was the fact that SVB had the highest percentage of uninsured domestic deposits of all big banks. These totaled nearly $152 billion, or about 97% of all deposits. By the end of the day, customers had tried to withdraw $42 billion in deposits.
What Triggered the SVB Collapse?
While the collapse of SVB took place over the course of 44 hours, its roots trace back to the early pandemic years. In 2021, U.S. venture capital-backed companies raised a record $330 billion—double the amount seen in 2020. At the time, interest rates were at rock-bottom levels to help buoy the economy. Matt Levine sums up the situation well: “When interest rates are low everywhere, a dollar in 20 years is about as good as a dollar today, so a startup whose business model is “we will lose money for a decade building artificial intelligence, and then rake in lots of money in the far future” sounds pretty good. When interest rates are higher, a dollar today is better than a dollar tomorrow, so investors want cash flows. When interest rates were low for a long time, and suddenly become high, all the money that was rushing to your customers is suddenly cut off.” Source: Pitchbook Why is this important? During this time, SVB received billions of dollars from these venture-backed clients. In one year alone, their deposits increased 100%. They took these funds and invested them in longer-term bonds. As a result, this created a dangerous trap as the company expected rates would remain low. During this time, SVB invested in bonds at the top of the market. As interest rates rose higher and bond prices declined, SVB started taking major losses on their long-term bond holdings.
Losses Fueling a Liquidity Crunch
When SVB reported its fourth quarter results in early 2023, Moody’s Investor Service, a credit rating agency took notice. In early March, it said that SVB was at high risk for a downgrade due to its significant unrealized losses. In response, SVB looked to sell $2 billion of its investments at a loss to help boost liquidity for its struggling balance sheet. Soon, more hedge funds and venture investors realized SVB could be on thin ice. Depositors withdrew funds in droves, spurring a liquidity squeeze and prompting California regulators and the FDIC to step in and shut down the bank.
What Happens Now?
While much of SVB’s activity was focused on the tech sector, the bank’s shocking collapse has rattled a financial sector that is already on edge.
The four biggest U.S. banks lost a combined $52 billion the day before the SVB collapse. On Friday, other banking stocks saw double-digit drops, including Signature Bank (-23%), First Republic (-15%), and Silvergate Capital (-11%).
Source: Morningstar Direct. *Represents March 9 data, trading halted on March 10.
When the dust settles, it’s hard to predict the ripple effects that will emerge from this dramatic event. For investors, the Secretary of the Treasury Janet Yellen announced confidence in the banking system remaining resilient, noting that regulators have the proper tools in response to the issue.
But others have seen trouble brewing as far back as 2020 (or earlier) when commercial banking assets were skyrocketing and banks were buying bonds when rates were low.