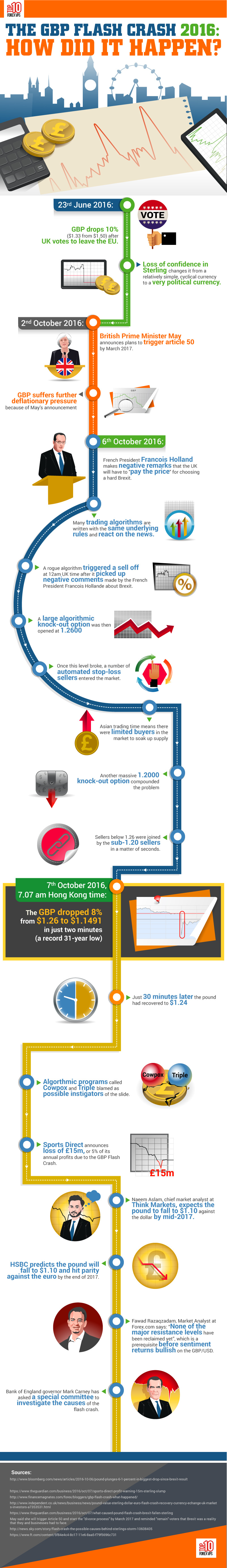
For better or worse, that statement applies to the financial world as well. It is said today that 75% of all financial market volume is automated, though there are lower and higher estimates out there depending on the report. The bottom line is that algorithmic trading is the dominant market player – and this has benefits and drawbacks for average investors. On the upside, markets are less volatile and presumably more rational because they are driven by computers instead of fallible humans. On the other hand? Sometimes algos just go rogue and do something unpredictable. When the British pound flash crashed earlier this month, it was exactly this latter thing that happened.
Explaining the October Flash Crash in the British Pound
The following infographic from Top 10 Forex VPS shares a play-by-play breakdown of how the British pound crashed a whopping 8% in just two minutes. It’s interesting because it helps give a sense of how the piping works behind these trading algorithms. It’s also a cautionary tale of algos gone wild, showing how market momentum can be swung in a particular direction even without your average market participants being involved.
In the aftermath of Brexit, the British pound has subsequently morphed into a “political” currency that seems to get most of its trading action based on commentary and speculation about the country’s eventual withdrawal from the EU. On October 6, 2016, François Hollande said that the UK must “pay the price” for Brexit. Trading algorithms reacted to this news that they deemed to be negative, and it triggered a GBP selloff. Once a massive knock-out option was opened and a certain price broke, it triggered a number of automated stop-loss sellers. After a few other algorithms kicked in, the British pound went from $1.26 to $1.1491 in a matter of just two minutes in USD terms. That’s a 8% slide in a globally significant currency. Just 30 minutes later, the pound recovered to more normal trading levels. The flash crash was just that – temporary. However, this does raise the question: what could have happened in a more extreme case of algos gone wild?
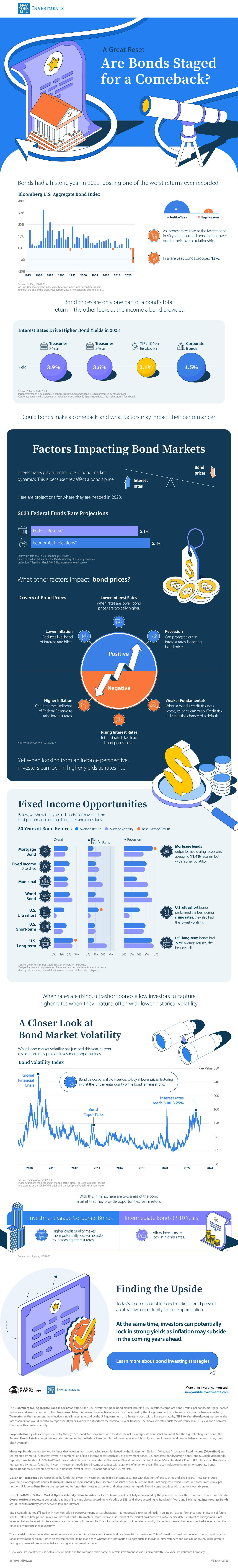
on The good news is that the Federal Reserve, U.S. Treasury, and Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation are taking action to restore confidence and take the appropriate measures to help provide stability in the market. With this in mind, the above infographic from New York Life Investments looks at the factors that impact bonds, how different types of bonds have historically performed across market environments, and the current bond market volatility in a broader context.
Bond Market Returns
Bonds had a historic year in 2022, posting one of the worst returns ever recorded. As interest rates rose at the fastest pace in 40 years, it pushed bond prices lower due to their inverse relationship. In a rare year, bonds dropped 13%.
Source: FactSet, 01/02/2023.
Bond prices are only one part of a bond’s total return—the other looks at the income a bond provides. As interest rates have increased in the last year, it has driven higher bond yields in 2023.
Source: YCharts, 3/20/2023.
With this recent performance in mind, let’s look at some other key factors that impact the bond market.
Factors Impacting Bond Markets
Interest rates play a central role in bond market dynamics. This is because they affect a bond’s price. When rates are rising, existing bonds with lower rates are less valuable and prices decline. When rates are dropping, existing bonds with higher rates are more valuable and their prices rise. In March, the Federal Reserve raised rates 25 basis points to fall within the 4.75%-5.00% range, a level not seen since September 2007. Here are projections for where the federal funds rate is headed in 2023:
Federal Reserve Projection*: 5.1% Economist Projections**: 5.3%
*Based on median estimates in the March summary of quarterly economic projections.**Projections based on March 10-15 Bloomberg economist survey. Together, interest rates and the macroenvironment can have a positive or negative effect on bonds.
Positive
Here are three variables that may affect bond prices in a positive direction:
Lower Inflation: Reduces likelihood of interest rate hikes. Lower Interest Rates: When rates are falling, bond prices are typically higher. Recession: Can prompt a cut in interest rates, boosting bond prices.
Negative
On the other hand, here are variables that may negatively impact bond prices:
Higher Inflation: Can increase the likelihood of the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates. Rising Interest Rates: Interest rate hikes lead bond prices to fall. Weaker Fundamentals: When a bond’s credit risk gets worse, its price can drop. Credit risk indicates the chance of a default, the risk of a bond issuer not making interest payments within a given time period.
Bonds have been impacted by these negative factors since inflation started rising in March 2021.
Fixed Income Opportunities
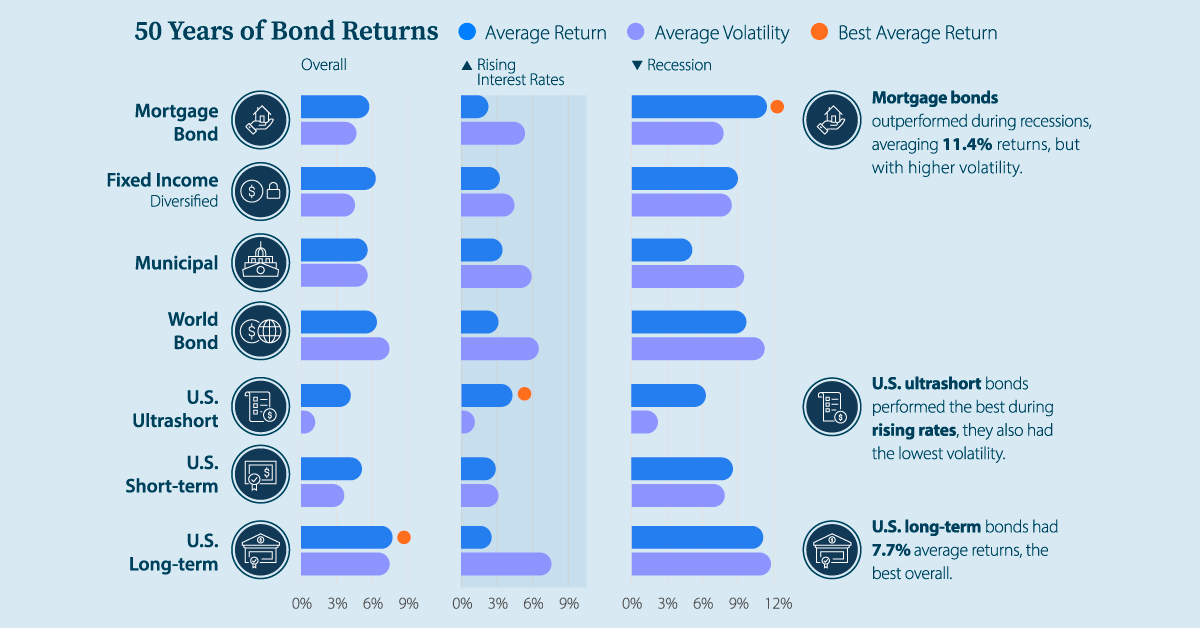
Below, we show the types of bonds that have had the best performance during rising rates and recessions.
Source: Derek Horstmeyer, George Mason University 12/3/2022. As we can see, U.S. ultrashort bonds performed the best during rising rates. Mortgage bonds outperformed during recessions, averaging 11.4% returns, but with higher volatility. U.S. long-term bonds had 7.7% average returns, the best across all market conditions. In fact, they were also a close second during recessions. When rates are rising, ultrashort bonds allow investors to capture higher rates when they mature, often with lower historical volatility.
A Closer Look at Bond Market Volatility
While bond market volatility has jumped this year, current dislocations may provide investment opportunities. Bond dislocations allow investors to buy at lower prices, factoring in that the fundamental quality of the bond remains strong. With this in mind, here are two areas of the bond market that may provide opportunities for investors:
Investment-Grade Corporate Bonds: Higher credit quality makes them potentially less vulnerable to increasing interest rates. Intermediate Bonds (2-10 Years): Allow investors to lock in higher rates.
Both types of bonds focus on quality and capturing higher yields when faced with challenging market conditions.
Finding the Upside
Much of the volatility seen in the banking sector was due to banks buying bonds during the pandemic—or even earlier—at a time when interest rates were historically low. Since then, rates have climbed considerably. Should rates moderate or stop increasing, this may present better market conditions for bonds. In this way, today’s steep discount in bond markets may present an attractive opportunity for price appreciation. At the same time, investors can potentially lock in strong yields as inflation may subside in the coming years ahead. Learn more about bond investing strategies with New York Life Investments.