It covers over 70% of the Earth’s surface, is home to millions of species of life, and it makes up 97% of all water on the planet. But, with this massive size and ubiquity also comes a significant challenge for humans interested in trade: it must be constantly traversed in order for us to move goods around. As a result, millions of people hit the high seas each day to get cargo from one place to another. The vessels used range from tiny sailboats to massive oil tankers, some of which can get up to four football fields in length.
Every Ship at Sea
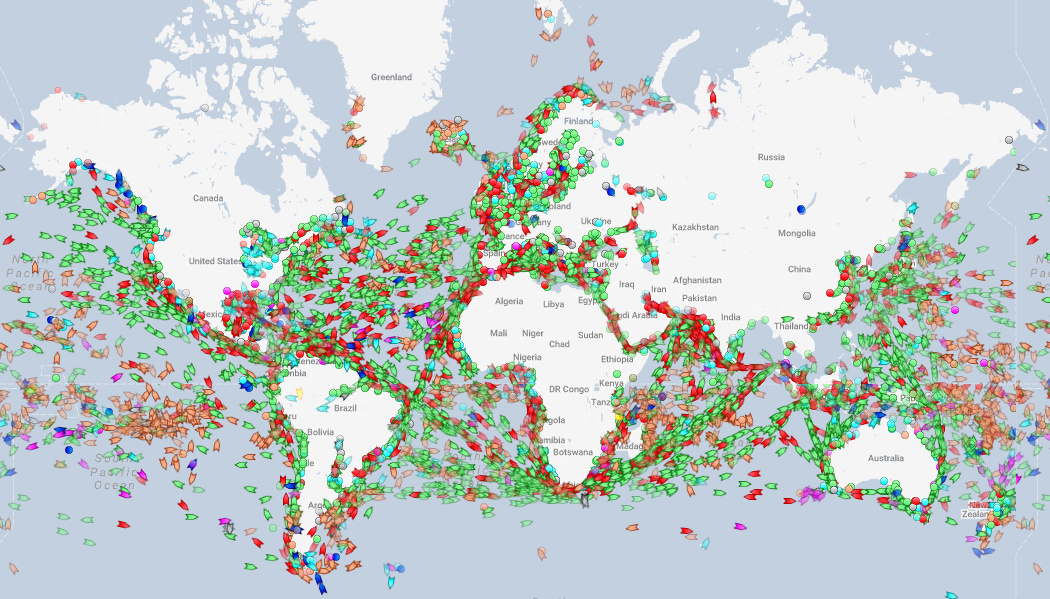
We previously posted an interactive map of shipping routes that used 250 million data points to show how boats moved across the ocean. Today, in a similar vein, we highlight a website that tracks the world’s ships in real-time, providing a unique picture of what is happening at sea. Below is a screenshot from MarineTraffic and going there will allow you to see all major ships in real-time as they voyage around the Deep Blue Sea.
You may be wondering, does this really show every ship at sea? Well, it might not catch your Uncle Steve’s sailboat off the coast of Florida, but this map will show all major commercial vessels. Any oil tanker, cargo vessel, cruise ship, or fishing boat can be spotted, and it makes for some interesting observations if you know where to look.
A Look at Oil Chokepoints
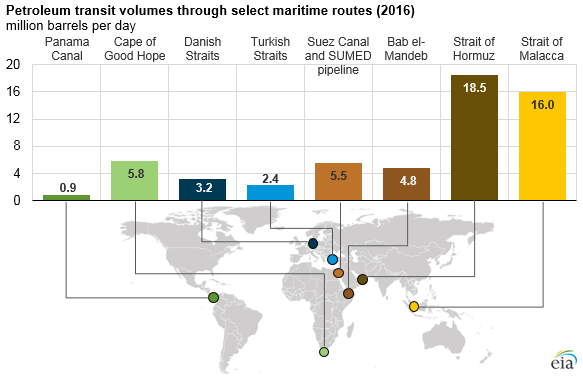
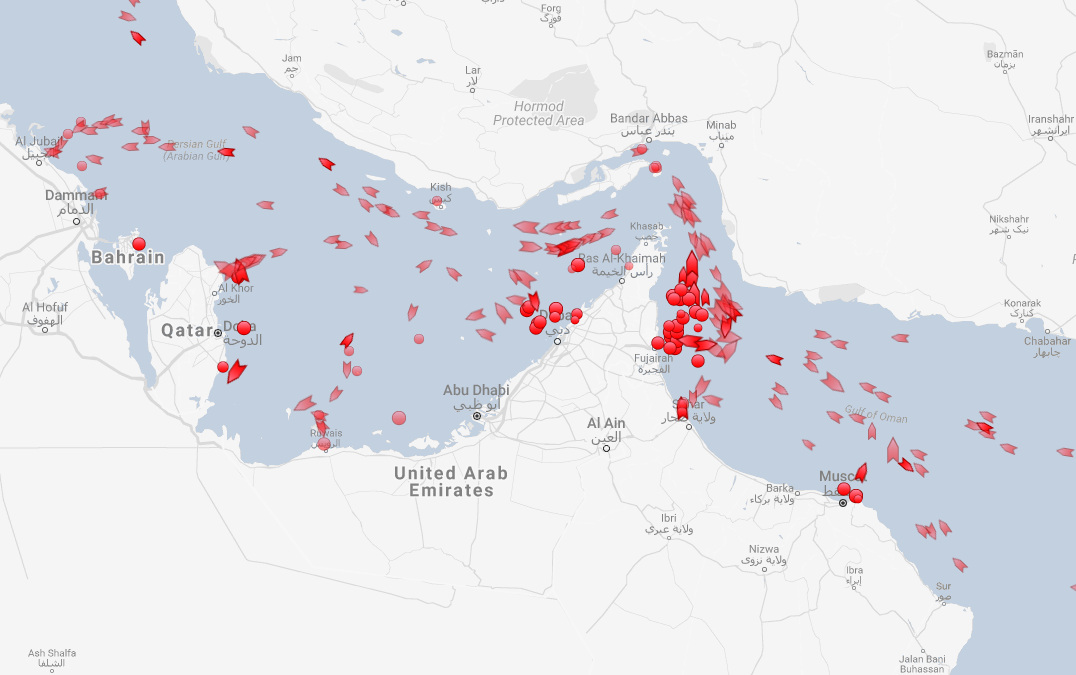
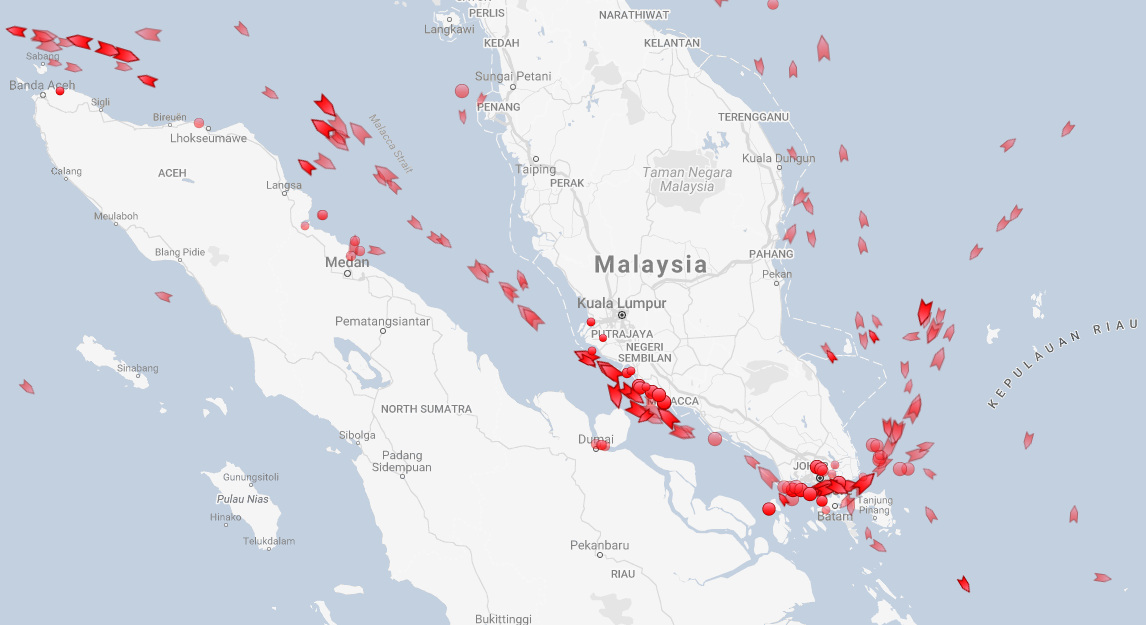
Upon loading the real-time map, the first thing we did was adjust the filters to only show oil tankers. After all, we know that every day, about 18.5 million barrels transit through the Strait of Hormuz between Iran and Oman, and 16 million barrels go through the Strait of Malacca between Indonesia and Malaysia.
Here’s a screenshot of the Strait of Hormuz, showing only oil tankers. (Dots are tankers that are not moving, while arrows represent tankers that are currently on course.)
And here are the ships going through the Strait of Malacca, which at its narrowest point is only 1.7 miles (2.7 km) wide.
If you want to get oil from the Persian Gulf to the South China Sea, this strait is vital – otherwise a big ship must detour thousands of miles around the Indonesian islands of Sumatra and Java to find the next suitable waterway.
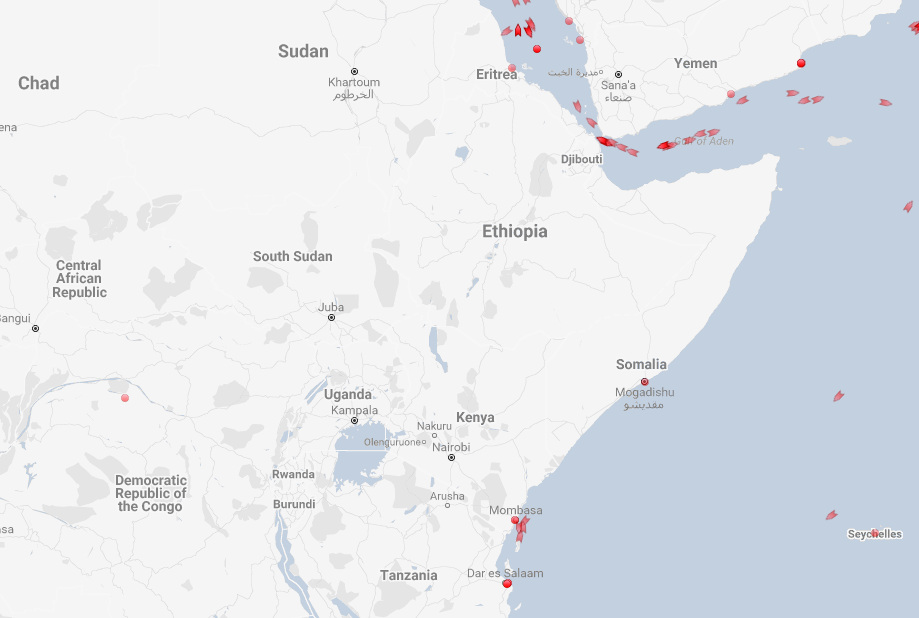
Coast of Somalia
Compare those above straits to the coast off of Somalia, where piracy and hydrocarbon theft are major concerns.
All is pretty quiet, aside from the one daring tanker that is about 500 miles (800 km) east of Mogadishu.
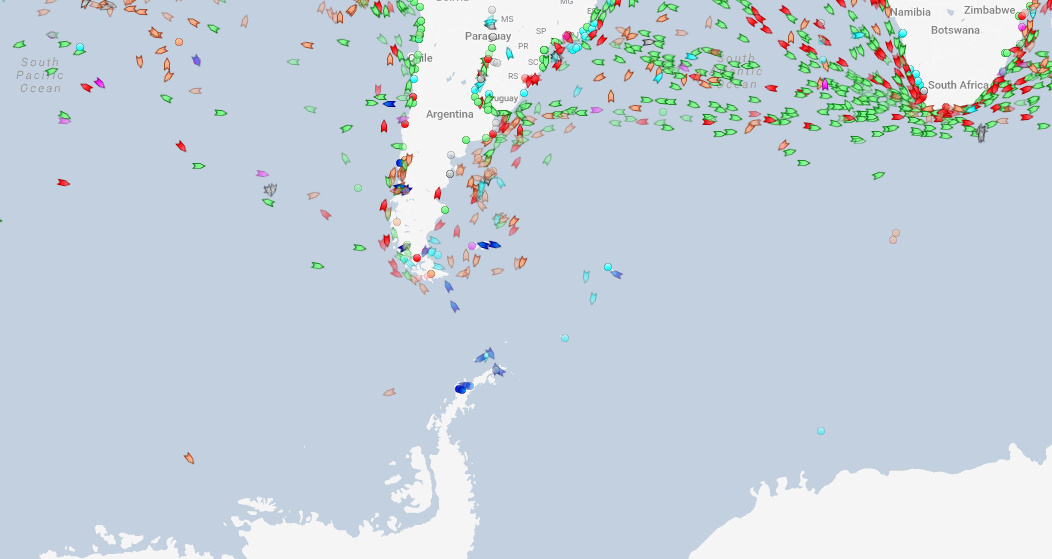
Antarctic Cruises
One other easy observation? It’s the few passenger boats hanging around the Antarctic Peninsula – which is the part of the continent closest to Argentina and a destination for cruise ships.
If you have a chance, check out the live map for yourself and play around with the filters. It’s also interesting to see what’s happening in your local waters, as well.
on Even while political regimes across these countries have changed over time, they’ve largely followed a few different types of governance. Today, every country can ultimately be classified into just nine broad forms of government systems. This map by Truman Du uses information from Wikipedia to map the government systems that rule the world today.
Countries By Type of Government
It’s important to note that this map charts government systems according to each country’s legal framework. Many countries have constitutions stating their de jure or legally recognized system of government, but their de facto or realized form of governance may be quite different. Here is a list of the stated government system of UN member states and observers as of January 2023: Let’s take a closer look at some of these systems.
Monarchies
Brought back into the spotlight after the death of Queen Elizabeth II of England in September 2022, this form of government has a single ruler. They carry titles from king and queen to sultan or emperor, and their government systems can be further divided into three modern types: constitutional, semi-constitutional, and absolute. A constitutional monarchy sees the monarch act as head of state within the parameters of a constitution, giving them little to no real power. For example, King Charles III is the head of 15 Commonwealth nations including Canada and Australia. However, each has their own head of government. On the other hand, a semi-constitutional monarchy lets the monarch or ruling royal family retain substantial political powers, as is the case in Jordan and Morocco. However, their monarchs still rule the country according to a democratic constitution and in concert with other institutions. Finally, an absolute monarchy is most like the monarchies of old, where the ruler has full power over governance, with modern examples including Saudi Arabia and Vatican City.
Republics
Unlike monarchies, the people hold the power in a republic government system, directly electing representatives to form government. Again, there are multiple types of modern republic governments: presidential, semi-presidential, and parliamentary. The presidential republic could be considered a direct progression from monarchies. This system has a strong and independent chief executive with extensive powers when it comes to domestic affairs and foreign policy. An example of this is the United States, where the President is both the head of state and the head of government. In a semi-presidential republic, the president is the head of state and has some executive powers that are independent of the legislature. However, the prime minister (or chancellor or equivalent title) is the head of government, responsible to the legislature along with the cabinet. Russia is a classic example of this type of government. The last type of republic system is parliamentary. In this system, the president is a figurehead, while the head of government holds real power and is validated by and accountable to the parliament. This type of system can be seen in Germany, Italy, and India and is akin to constitutional monarchies. It’s also important to point out that some parliamentary republic systems operate slightly differently. For example in South Africa, the president is both the head of state and government, but is elected directly by the legislature. This leaves them (and their ministries) potentially subject to parliamentary confidence.
One-Party State
Many of the systems above involve multiple political parties vying to rule and govern their respective countries. In a one-party state, also called a single-party state or single-party system, only one political party has the right to form government. All other political parties are either outlawed or only allowed limited participation in elections. In this system, a country’s head of state and head of government can be executive or ceremonial but political power is constitutionally linked to a single political movement. China is the most well-known example of this government system, with the General Secretary of the Communist Party of China ruling as the de facto leader since 1989.
Provisional
The final form of government is a provisional government formed as an interim or transitional government. In this system, an emergency governmental body is created to manage political transitions after the collapse of a government, or when a new state is formed. Often these evolve into fully constitutionalized systems, but sometimes they hold power for longer than expected. Some examples of countries that are considered provisional include Libya, Burkina Faso, and Chad.