The world has become increasingly fascinated with cryptocurrencies and the ways they are enabling greater access, such as being able to send funds to remote places or securing capital for small businesses. To aid this, cryptocurrency regulations are being slowly introduced into global financial markets. Regulations help to monitor these emerging digital currencies, and to allow for clearer guidelines and a measure of security.
The Regulatory Landscape
Today’s graphic from ComplyAdvantage maps out major regulatory cryptocurrency and exchange landscapes around the world, showing how sentiments towards digital currencies are evolving. To do this, ComplyAdvantage measured cryptocurrency regulatory environments using their own Light-to-Tight scale, based on the following criteria:
Cryptocurrencies and exchanges status? (Ban = 3 points, Regulated = 2 points, Grey Area = 1 point) Cryptocurrency considered legal tender? (Yes = 1 point, No = 0 points) Planned legislation to increase crypto regulation? (Yes = 1 point, No = 0 points)
Which jurisdictions have the strictest and most relaxed regulations for cryptocurrencies?
Regulations by Region
Global attitudes towards the rise of cryptocurrencies have shifted greatly over the past few years. While the term cryptocurrency is a bit of a misnomer, some countries do consider digital currencies legal tender, with many viewing cryptocurrencies as commodities. Below is a table of the major countries that are pursuing cryptocurrency regulations: Sources: ComplyAdvantage, HedgeTrade, CoinDesk
Asia
Japan has one of the most progressive regulatory climates for cryptocurrencies, widely considering bitcoin as legal tender and passing a law in mid-2017 recognizing cryptocurrencies as legal property. In late 2018, Japan also approved self-regulation for the crypto industry. By contrast, China currently has one of the most restrictive environments in the world for cryptocurrency. China banned bitcoin transactions in 2013, as well as ICOs and crypto exchanges in 2017─though many have found workarounds through sites not yet firewalled.
Europe
Cryptocurrency and exchange regulations in the EU are determined by individual member states, and are considered legal across the bloc. —Christine Lagarde, Managing Director of IMF Perhaps unsurprisingly, Switzerland has one of the most open climates for cryptocurrencies and exchanges in Europe. In 2016, the city of Zug, known as “Crypto Valley”, started accepting bitcoin as payment for city fees. Swiss Economics Minister Johann Schneider-Ammann announced his goal in 2018 to make Switzerland the world’s first “crypto-nation”.
North America
Both Canada and the U.S. take a similar approach to cryptocurrency legislation at the federal level, as both countries view cryptocurrencies as securities. However, provincial and state regulations differ widely in their taxation requirements of profits from crypto investments.
Latin America
Regulations throughout Latin and South America run the full legislative spectrum.
Bolivia: unilateral ban on cryptocurrencies and exchanges Ecuador: the first country to launch its own token; ban on all cryptocurrencies aside from its government-issued SDE token (Sistema de Dinero Electrónico = electronic money system) Mexico, Argentina, Brazil, Chile: cryptocurrencies widely accepted as payment Venezuela: cryptocurrencies widely accepted; this makes sense, considering the economic crisis and subsequent freefall of the bolívar
The Importance of Cryptocurrency Regulations
Cryptocurrency’s journey is the story of a technology rapidly outpacing the laws that govern it. Governments around the world are keenly aware of this problem. Members of the G20 published a request in June 2019 for a global regulatory framework for cryptocurrencies to be implemented to better manage the benefits and challenges that cryptocurrencies bring. Regulation for both cryptocurrencies and crypto exchanges is essential for the future of digital finance─bringing legitimacy to the digital financial market, and making it more attractive for new businesses, established banks, and investors worldwide to more easily conduct business within this emerging ecosystem. on But fast forward to the end of last week, and SVB was shuttered by regulators after a panic-induced bank run. So, how exactly did this happen? We dig in below.
Road to a Bank Run
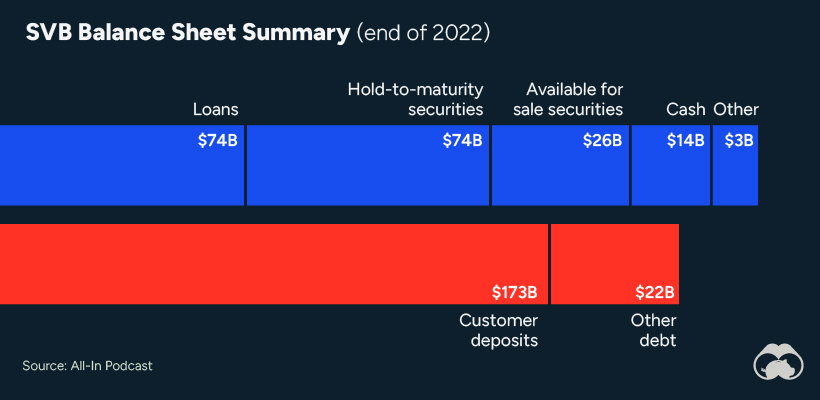
SVB and its customers generally thrived during the low interest rate era, but as rates rose, SVB found itself more exposed to risk than a typical bank. Even so, at the end of 2022, the bank’s balance sheet showed no cause for alarm.
As well, the bank was viewed positively in a number of places. Most Wall Street analyst ratings were overwhelmingly positive on the bank’s stock, and Forbes had just added the bank to its Financial All-Stars list. Outward signs of trouble emerged on Wednesday, March 8th, when SVB surprised investors with news that the bank needed to raise more than $2 billion to shore up its balance sheet. The reaction from prominent venture capitalists was not positive, with Coatue Management, Union Square Ventures, and Peter Thiel’s Founders Fund moving to limit exposure to the 40-year-old bank. The influence of these firms is believed to have added fuel to the fire, and a bank run ensued. Also influencing decision making was the fact that SVB had the highest percentage of uninsured domestic deposits of all big banks. These totaled nearly $152 billion, or about 97% of all deposits. By the end of the day, customers had tried to withdraw $42 billion in deposits.
What Triggered the SVB Collapse?
While the collapse of SVB took place over the course of 44 hours, its roots trace back to the early pandemic years. In 2021, U.S. venture capital-backed companies raised a record $330 billion—double the amount seen in 2020. At the time, interest rates were at rock-bottom levels to help buoy the economy. Matt Levine sums up the situation well: “When interest rates are low everywhere, a dollar in 20 years is about as good as a dollar today, so a startup whose business model is “we will lose money for a decade building artificial intelligence, and then rake in lots of money in the far future” sounds pretty good. When interest rates are higher, a dollar today is better than a dollar tomorrow, so investors want cash flows. When interest rates were low for a long time, and suddenly become high, all the money that was rushing to your customers is suddenly cut off.” Source: Pitchbook Why is this important? During this time, SVB received billions of dollars from these venture-backed clients. In one year alone, their deposits increased 100%. They took these funds and invested them in longer-term bonds. As a result, this created a dangerous trap as the company expected rates would remain low. During this time, SVB invested in bonds at the top of the market. As interest rates rose higher and bond prices declined, SVB started taking major losses on their long-term bond holdings.
Losses Fueling a Liquidity Crunch
When SVB reported its fourth quarter results in early 2023, Moody’s Investor Service, a credit rating agency took notice. In early March, it said that SVB was at high risk for a downgrade due to its significant unrealized losses. In response, SVB looked to sell $2 billion of its investments at a loss to help boost liquidity for its struggling balance sheet. Soon, more hedge funds and venture investors realized SVB could be on thin ice. Depositors withdrew funds in droves, spurring a liquidity squeeze and prompting California regulators and the FDIC to step in and shut down the bank.
What Happens Now?
While much of SVB’s activity was focused on the tech sector, the bank’s shocking collapse has rattled a financial sector that is already on edge.
The four biggest U.S. banks lost a combined $52 billion the day before the SVB collapse. On Friday, other banking stocks saw double-digit drops, including Signature Bank (-23%), First Republic (-15%), and Silvergate Capital (-11%).
Source: Morningstar Direct. *Represents March 9 data, trading halted on March 10.
When the dust settles, it’s hard to predict the ripple effects that will emerge from this dramatic event. For investors, the Secretary of the Treasury Janet Yellen announced confidence in the banking system remaining resilient, noting that regulators have the proper tools in response to the issue.
But others have seen trouble brewing as far back as 2020 (or earlier) when commercial banking assets were skyrocketing and banks were buying bonds when rates were low.