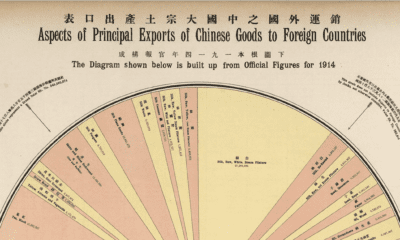
The History of Jade: The Emperor’s Stone
Infographic presented by Electra Stone In Chinese writing, it is no accident that the character for “emperor” looks almost identical to the character for “jade”. In the West, precious gems such as diamonds or rubies were worn by high-ranking people as status symbols. However, in China, it is jade that has been a symbol of status, spirituality, purity, and health for over 9,000 years.
The Origins of Jade
Jade has been mined and worked in China since the Stone Age. In prehistoric sites, jade artifacts include simple ornaments with bead, button, and tubular shapes. It was also used for tools and weapons. Jade later became revered with special significance. Beautiful designs were used for carvings, decorations, ceremonies, furnishings, and jewelry for the Imperial families. By 3,000 BC, jade became known as “yu” or the “royal gem”. Xu Shen, from the Han Dynasty (206 BC to 221 AD), details the five virtues of jade in his work Shuowen Jiezi: Benevolence for its lustre and brilliance. Honesty for its translucent texture. Wisdom for its tranquil and far-reaching tone. Integrity and Bravery for it may be broken but cannot be twisted. The most wealthy and influential members of society would be buried in jade suits. Extremely costly and taking years to assemble, the thread used to join the pieces of jade would be gold, silver, copper, silk, or other materials depending on the status of the person buried. The first archaeological discoveries of these suits, of Prince Liu Sheng and Dou Wan of the Western Han dynasty, consisted of: 2498 pieces of jade and 2.5 lbs of gold wire. The gemstone’s significance to Chinese culture cannot be understated. Entire kingdoms in China have started wars over particularly precious stones.
What is Jade?
Jade is different than other types of valuable gems or precious metals. In fact, the cultural term “jade” refers to two different and similar types of ornamental rocks, both made of different silicate minerals. Nephrite jade was the very first of these materials discovered in China, and was the traditional jade used and carved since ancient times. Nephrite was so important that the traditional deposits in China are now all but depleted. There is evidence that jadeite jade, coming primarily from Burma, began to be traded in China on a wider scale in the 14th century. It was harder, denser, and worked easier – it eventually became the form of the gemstone preferred by Chinese artisans and prized by the Chinese people. Today, most jade traded in China is of the jadeite variety. However, the country’s traditional nephrite jade is not forgotten. Every athlete’s medal, at the 2008 Beijing Olympics, was embedded with a piece of pure, natural-carved jade. The gold medal featured a rare form of white nephrite known as “mutton fat” jade.
The Value of Jade
Jade is valued differently than other comparable gemstones or precious metals. Jade is not fungible like gold, and jade is not a single polished and cut crystal, such as in the case of diamonds or rubies. Both jadeite and nephrite jade are stones formed of interlocking microcrystals. Jade comes in different shapes and sizes, and can have impurities or grains in the stone that define its character. This means each piece of jade is unique. Professional craftsmen look at raw jade’s beauty, flaws, and spirit to determine what shall be carved from it. This potential ties into the price that people are willing to pay for it. Jade jewelry and artwork are extremely important to China’s culture and history. This is why buyers are willing to pay a steep price for the finest jade. What does the best jade sell for in China? It sells for the same price per carat as diamonds in the United States.
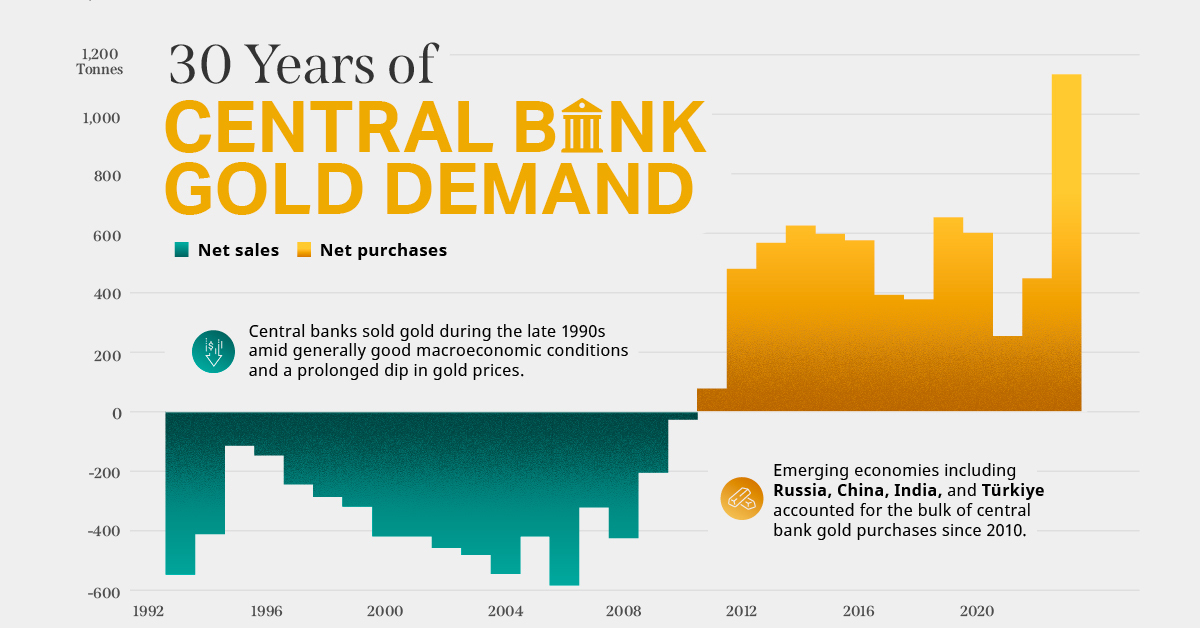
on Did you know that nearly one-fifth of all the gold ever mined is held by central banks? Besides investors and jewelry consumers, central banks are a major source of gold demand. In fact, in 2022, central banks snapped up gold at the fastest pace since 1967. However, the record gold purchases of 2022 are in stark contrast to the 1990s and early 2000s, when central banks were net sellers of gold. The above infographic uses data from the World Gold Council to show 30 years of central bank gold demand, highlighting how official attitudes toward gold have changed in the last 30 years.
Why Do Central Banks Buy Gold?
Gold plays an important role in the financial reserves of numerous nations. Here are three of the reasons why central banks hold gold:
Balancing foreign exchange reserves Central banks have long held gold as part of their reserves to manage risk from currency holdings and to promote stability during economic turmoil. Hedging against fiat currencies Gold offers a hedge against the eroding purchasing power of currencies (mainly the U.S. dollar) due to inflation. Diversifying portfolios Gold has an inverse correlation with the U.S. dollar. When the dollar falls in value, gold prices tend to rise, protecting central banks from volatility. The Switch from Selling to Buying In the 1990s and early 2000s, central banks were net sellers of gold. There were several reasons behind the selling, including good macroeconomic conditions and a downward trend in gold prices. Due to strong economic growth, gold’s safe-haven properties were less valuable, and low returns made it unattractive as an investment. Central bank attitudes toward gold started changing following the 1997 Asian financial crisis and then later, the 2007–08 financial crisis. Since 2010, central banks have been net buyers of gold on an annual basis. Here’s a look at the 10 largest official buyers of gold from the end of 1999 to end of 2021: Rank CountryAmount of Gold Bought (tonnes)% of All Buying #1🇷🇺 Russia 1,88828% #2🇨🇳 China 1,55223% #3🇹🇷 Türkiye 5418% #4🇮🇳 India 3956% #5🇰🇿 Kazakhstan 3455% #6🇺🇿 Uzbekistan 3115% #7🇸🇦 Saudi Arabia 1803% #8🇹🇭 Thailand 1682% #9🇵🇱 Poland1282% #10🇲🇽 Mexico 1152% Total5,62384% Source: IMF The top 10 official buyers of gold between end-1999 and end-2021 represent 84% of all the gold bought by central banks during this period. Russia and China—arguably the United States’ top geopolitical rivals—have been the largest gold buyers over the last two decades. Russia, in particular, accelerated its gold purchases after being hit by Western sanctions following its annexation of Crimea in 2014. Interestingly, the majority of nations on the above list are emerging economies. These countries have likely been stockpiling gold to hedge against financial and geopolitical risks affecting currencies, primarily the U.S. dollar. Meanwhile, European nations including Switzerland, France, Netherlands, and the UK were the largest sellers of gold between 1999 and 2021, under the Central Bank Gold Agreement (CBGA) framework. Which Central Banks Bought Gold in 2022? In 2022, central banks bought a record 1,136 tonnes of gold, worth around $70 billion. Country2022 Gold Purchases (tonnes)% of Total 🇹🇷 Türkiye14813% 🇨🇳 China 625% 🇪🇬 Egypt 474% 🇶🇦 Qatar333% 🇮🇶 Iraq 343% 🇮🇳 India 333% 🇦🇪 UAE 252% 🇰🇬 Kyrgyzstan 61% 🇹🇯 Tajikistan 40.4% 🇪🇨 Ecuador 30.3% 🌍 Unreported 74165% Total1,136100% Türkiye, experiencing 86% year-over-year inflation as of October 2022, was the largest buyer, adding 148 tonnes to its reserves. China continued its gold-buying spree with 62 tonnes added in the months of November and December, amid rising geopolitical tensions with the United States. Overall, emerging markets continued the trend that started in the 2000s, accounting for the bulk of gold purchases. Meanwhile, a significant two-thirds, or 741 tonnes of official gold purchases were unreported in 2022. According to analysts, unreported gold purchases are likely to have come from countries like China and Russia, who are looking to de-dollarize global trade to circumvent Western sanctions.
There were several reasons behind the selling, including good macroeconomic conditions and a downward trend in gold prices. Due to strong economic growth, gold’s safe-haven properties were less valuable, and low returns made it unattractive as an investment.
Central bank attitudes toward gold started changing following the 1997 Asian financial crisis and then later, the 2007–08 financial crisis. Since 2010, central banks have been net buyers of gold on an annual basis.
Here’s a look at the 10 largest official buyers of gold from the end of 1999 to end of 2021:
Source: IMF
The top 10 official buyers of gold between end-1999 and end-2021 represent 84% of all the gold bought by central banks during this period.
Russia and China—arguably the United States’ top geopolitical rivals—have been the largest gold buyers over the last two decades. Russia, in particular, accelerated its gold purchases after being hit by Western sanctions following its annexation of Crimea in 2014.
Interestingly, the majority of nations on the above list are emerging economies. These countries have likely been stockpiling gold to hedge against financial and geopolitical risks affecting currencies, primarily the U.S. dollar.
Meanwhile, European nations including Switzerland, France, Netherlands, and the UK were the largest sellers of gold between 1999 and 2021, under the Central Bank Gold Agreement (CBGA) framework.
Which Central Banks Bought Gold in 2022?
In 2022, central banks bought a record 1,136 tonnes of gold, worth around $70 billion. Türkiye, experiencing 86% year-over-year inflation as of October 2022, was the largest buyer, adding 148 tonnes to its reserves. China continued its gold-buying spree with 62 tonnes added in the months of November and December, amid rising geopolitical tensions with the United States. Overall, emerging markets continued the trend that started in the 2000s, accounting for the bulk of gold purchases. Meanwhile, a significant two-thirds, or 741 tonnes of official gold purchases were unreported in 2022. According to analysts, unreported gold purchases are likely to have come from countries like China and Russia, who are looking to de-dollarize global trade to circumvent Western sanctions.